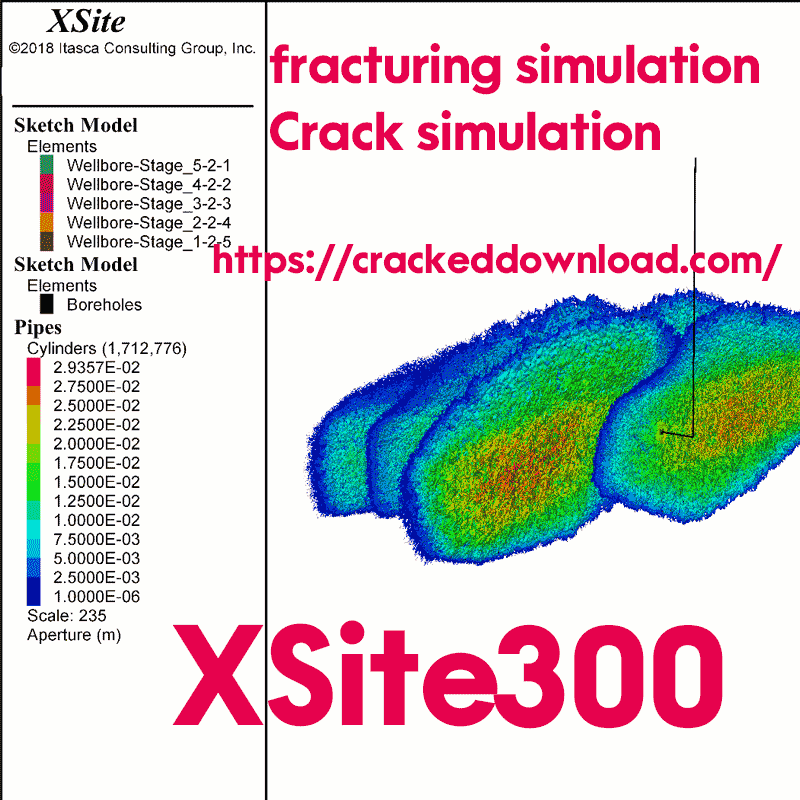
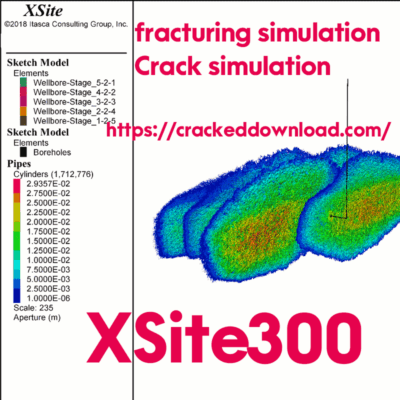
XSite 300 hydraulic fracturing simulation Crack simulation
€0.00
XSite 300, crack license XSite 300
XSite 300 hydraulic fracturing simulation Crack simulation, how to download XSite 300 crack license working tested.Elevate your geotechnical and hydrogeological problem-solving with XSite. Essential for hydraulic fracturing simulations of your energy or mining operation.
XSite 300 hydraulic fracturing simulation Crack simulation
High-performance numerical simulation · Fast and accurate hydraulic fracturing modeling · Efficient multi-threaded processing for quicker results
XSite is a special-purpose software package designed to meet the needs of hydraulic fracturing simulation. Main features available with XSite include:
- No assumptions regarding the fracture shape or trajectory
- Fracture propagation in inhomogeneous and naturally fractured rock masses
- Interactions between hydraulic fractures, joints, and between stages and wells (including the stress shadow effect and hydraulic connectivity) are accounted for
- In situ stresses may be specified
- Arbitrary number of wellbores and injection points
- Synthetic microseismicity is generated as the fractures slip or propagate, providing a method for model calibration with field observations
- Non-steady fluid flow within joints and the intact rock
- Proppant transport and placement
- Thermal analysis
- Heat conduction (and thermo-mechanical effects) in the rock and heat exchange with the fluid in fractures can be simulated
- Approximated heat advection by injected fluid
- Easy setup of models for multi-stage simulation
The model shown below simulates open-hole, sliding-sleeve hydraulic stimulation along the horizontal section of the borehole. Five stages are included in the model. The Sh,min in 50-m high reservoir is 30 MPa. The verical stress and SH,max are 42 MPa. The stress barrier between the reservoir and underburden and overburden is approximately 2 MPa. The horizontal segment of the borehole is oriented in the direction of Sh,min. For the sake of simplicity, the DFN was not explicitly represented in this model. For each stage, slick water was injected for 33 minutes at a rate of 11 m3/min.
Supplemental Files
The following DLL library file must be installed before running XSite 3.0 for the first time.
msmpisetup.exe (5.9 MB, Stand-alone, redistributable and SDK installers for Microsoft MPI)
Known Issues
- The maximum proppant concentration is still hardwired to 0.7. It should probably increased to 1.0
- Need to take a closer look at proppant stress when the new conductivity curves (indexed by proppant concentration and stress) are used.
- Perforated tunnels:
- Simplified logic cluster volume calculation needs to take in consideration that the part of the perf. tunnel cylinder is already taken into consideration by the borehole volume;
- Generalize the logic for viscosity transition allowing switch from power-law fluid and include power-law fluid and fluid transition in the simplified logic; and
- resetClusterOnNodes is called after a stage is inactivated; it probably should not to avoid premature connection of the active fractures with those connected with inactive clusters.
- Export grid function is limited to infinite horizontal plane seams. Will added ability to specify export extent based on top and lower seam for minimum and maximum Z coordinate and fractures location for X and Y coordinates.
XSite 3.00 64-bit Update
Hydraulic Fracture Simulation of 3D Fracture Networks
Elevate your geotechnical and hydrogeological problem-solving with XSite. Essential for hydraulic fracturing simulations of your energy or mining operation. Optimize solutions now with XSite!
Why Choose XSite?
Explore XSite‘s comprehensive features and user-friendly interface. Unlock powerful computing capabilities, including the ability to run two models simultaneously. Discover why XSite is the ideal choice:
Applications
- Reservoir-scale, multi-well, multi-stage field stimulation by multiple fracture propagation with application to both petroleum, Engineered Geothermal System (EGS), and rock mass preconditioning (mining industry) operations
- Simulation of fracture propagation on reservoir scales
- Near-wellbore models to simulate fracture initiation
- Proppant transport and placement
- Prediction of microseismicity
- Rock mass preconditioning for mining operations
Analysis
- Mechanical (statics, small-strain)
- Fluid Flow
- Microseismics
- Thermal analysis
- Proppant
- Lattice Method
- Synthetic Rock Mass
- Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical coupling
- Hydraulic fracturing
- Heat conduction, advection, and convective heat exchange
Ease of Use
- Streamlined modeling and simulation workflows
- Automated processes for efficient modeling
- GUI that allows visualization of model setup and results
- Built-in logic for proppant transport and fracture interaction
- User-friendly settings for simulations
- Integrated borehole flow calculations
- Automated tracking and recording of synthetic microseismicity
- Easy and fast model discretization
- Easy and automated setup of multistage stimulation from multiple wells
- Capability to reuse model components (e.g., pumping schedule, well geometry, stage and cluster design)
Speed
- High-performance numerical simulation
- Fast and accurate hydraulic fracturing modeling
- Efficient multi-threaded processing for quicker results
- Implicit scheme for fluid flow simulation
- Rapid resolution of hydraulic fracture interactions
- Speedy modeling of multiple wellbores, stages, and clusters
- Optimized simulations of THM coupled processes including sub-stepping and multistepping
- Fast scheme for simulation of loosely coupled THM processes during long-term fluid circulation
- Fast simplified logic for simulation of hydraulic fracture propagation in the toughness-dominated regime
- Quick calculation of proppant transport and fracture interaction
- Swift tracking and recording of synthetic microseismicity
Powerful Capabilities
- Three-dimensional hydraulic fracturing simulation on reservoir scales
- Hydraulic fracturing of naturally fractured reservoirs
- Simulates reservoir stimulation due to hydraulic fracturing and hydro-shearing (i.e., slip on pre-existing fractures)
- Utilizes Synthetic Rock Mass (SRM) and Lattice methods
- Models multiple wellbores with multiple stages and clusters
- Simulates three-dimensional fracture initiation from open-hole completions and perforation tunnels
- Resolves hydraulic fracture interactions, including those in naturally fractured reservoirs
- Incorporates deterministically or stochastically generated discrete fracture networks (DFNs)
- Conducts fully coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical simulations
- Heat transport models include heat conduction, advection, and convective heat exchange
- Simulates fluid flow within fracture networks and matrix flow within the intact rock
- Simulates the effects of thermally induced stress changes during long-term circulation on permeability change
- Includes proppant transport and placement logic
- Accounts for proppant’s impact on fracture closure and conductivity
- Generates synthetic microseismicity due to fracture propagation and slip on pre-existing fractures
Flexibility
- Versatile three-dimensional hydraulic fracturing simulation
- Adaptable to various wellbore configurations, including open-hole completions and perforation tunnels
- Accommodates hydraulic fracture scenarios in different reservoirs (conventional and unconventional), including those in naturally fractured reservoirs
- Simulation of hydraulic fracturing in different regimes (viscosity-dominated, toughness-dominated, leakoff-dominated) or any transitional regime
- Supports deterministic or stochastic discrete fracture network (DFN) generation
- Customizable thermo-hydro-mechanical simulations
- Flexible leakoff modeling including matrix flow and Carter leakoff
- Adjustable proppant transport and placement options
- Adaptable borehole flow calculations for various cluster configurations
- Tailorable tracking and recording of synthetic microseismicity
- Recorded microseismicity can be imported and compared with microseismicity predicted by the model
- Upscales and exports results (e.g., permeability and porosity fields) to be used by reservoir simulators
Related products
Uncategorized
Science Research
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Mathematical
Geology
Simulation
scientific software
Dental Software
Science Research
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Mathematical
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Mining Industry
Uncategorized
Mathematical
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
chemistry software
Science Research
Cad/Cam
Mining Industry
unlimited find
Uncategorized
Science Research
engineering softwares
Geology
Science Research
Uncategorized
unlimited find
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Geology
Cad/Cam
Simulation
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Oil and Gas
Uncategorized
Biomedical
unlimited find